Table of Contents
Ai Modules
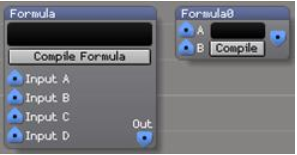
Formula
| section | Math |
|---|---|
| short description | Outputs a value calculated from the input value(s), with an easy-to-use formula language. |
| licence level | Anjuna |
| ports | Input A [numeric/control] Input B [numeric/control] Input C [numeric/control] Input D [numeric/control] Out [numeric/control] Compile Formula [pushbutton] |
| skins | Small, Medium |
Type in the formula, wire inputs and output, hit Compile. Now the output value is dynamically computed from the input value(s).
used in example
Manual
Applies a user defined formula to the inputs and outputs the value on the Out port. The formula syntax follows the mu parser format as specifed here: http://muparser.beltoforion.de/ with a few additional functions such as the Modulus function mod(a, b) and the addition of vector component access in the Vector Formula module.
Skins
Medium
4 inputs, medium-sized formula textfield. Can be resized.
Small
2 inputs, slightly smaller formula textfield. Can be resized.
Formula language
Currently a list of the available commands is available here: http://beltoforion.de/article.php?a=muparser&hl=en&p=features&da=1.
For ease of use it is replicated here, however, as always you are reeferred to the original source.
Built-in functions
The following table gives an overview of the functions supported by the default implementation. It lists the function names, the number of arguments and a brief description.
| Name | Argc. | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| sin | 1 | sine function |
| cos | 1 | cosine function |
| tan | 1 | tangens function |
| asin | 1 | arcus sine function |
| acos | 1 | arcus cosine function |
| atan | 1 | arcus tangens function |
| sinh | 1 | hyperbolic sine function |
| cosh | 1 | hyperbolic cosine |
| tanh | 1 | hyperbolic tangens function |
| asinh | 1 | hyperbolic arcus sine function |
| acosh | 1 | hyperbolic arcus tangens function |
| atanh | 1 | hyperbolic arcus tangens function |
| log2 | 1 | logarithm to the base 2 |
| log10 | 1 | logarithm to the base 10 |
| log | 1 | logarithm to base e (2.71828…) |
| ln | 1 | logarithm to base e (2.71828…) |
| exp | 1 | e raised to the power of x |
| sqrt | 1 | square root of a value |
| sign | 1 | sign function -1 if x<0; 1 if x>0 |
| rint | 1 | round to nearest integer |
| abs | 1 | absolute value |
| min | var. | min of all arguments |
| max | var. | max of all arguments |
| sum | var. | sum of all arguments |
| avg | var. | mean value of all arguments |
Built-in binary operators
The following table lists the default binary operators supported by the parser.
| Operator | Description | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| = | assignement | -1 |
| && | logical and | 1 |
| || | logical or | 2 |
| ⇐ | less or equal | 4 |
| >= | greater or equal | 4 |
| != | not equal | 4 |
| == | equal | 4 |
| > | greater than | 4 |
| < | less than | 4 |
| + | addition | 5 |
| - | subtraction | 5 |
| * | multiplication | 6 |
| / | division | 6 |
| ^ | raise x to the power of y | 7 |
- The assignment operator is special since it changes one of its arguments and can only by applied to variables.
Ternary Operators
muParser has built in support for the if then else operator. It uses lazy evaluation in order to make sure only the necessary branch of the expression is evaluated.
| Operator | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| ?: | if then else operator | C++ style syntax |